CAZN offers AVG cars a variety of connection solutions, both wireless and wired.
As artificial intelligence technology continues to advance and factory automation increases, the demand for various types of robots has become increasingly strong, with automated guided vehicles (AGVs) for transportation standing out prominently due to their intelligent features. AGVs offer the advantages of a simple structure, space-saving design, mobility, and flexibility, enabling cost savings on labor and improving production efficiency.
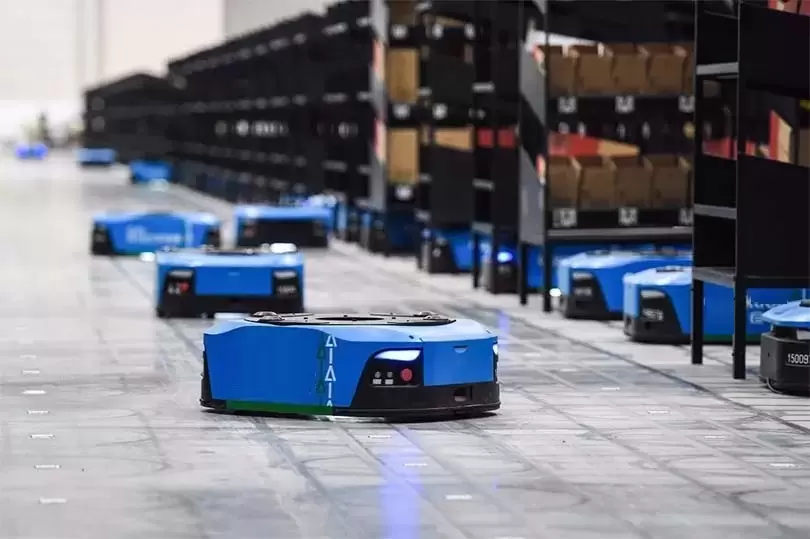

In warehouse operations, there are multiple guidance methods for transportation robots, including electromagnetic induction, lasers, infrared, and vision-based systems. These methods are used to identify the current position and movement trajectory of the robot, which are then compared and calibrated in real-time with a preset digital map trajectory stored internally. Ultimately, this allows the robot to automatically transport goods along a predetermined path. This process involves the application of various industrial connectors. Power connectors are required to supply electricity from the vehicle-mounted battery to motors, transmitters, and other devices on the AGV. Signal connectors are needed to transmit signals collected by sensors to control units such as vehicle-mounted microcontrollers.
- PrevLearn more+No Prev
- NextLearn more+No Next