M8 Circular Connectors vs. Other Connectors: What’s the Difference?
When it comes to choosing connectors for industrial applications, the options can be overwhelming. Among the many types of connectors, M8 circular connectors stand out due to their compact design, robust performance, and wide range of applications in industries like wind power generation, high-speed rail, automotive manufacturing, intelligent transportation, and smart manufacturing. But how do M8 connectors compare to other connector types, and what makes them the ideal choice for certain industries? In this blog, we’ll take a closer look at M8 circular connectors and compare them with other connector types, highlighting the differences, advantages, and ideal use cases.
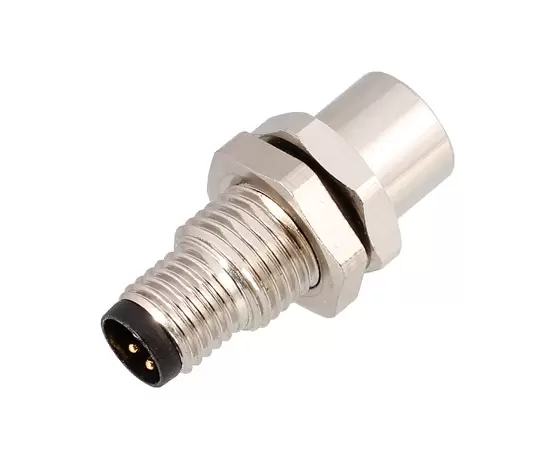

What Are M8 Circular Connectors?
M8 circular connectors are small, rugged connectors designed for industrial use, characterized by their 8mm diameter. These connectors are often used in automation and sensor-based systems, where space is limited, but reliable electrical connections are essential. The M8 connectors are designed to be easy to install, providing secure, high-performance connections in environments that demand both compactness and durability.
M8 connectors typically come in configurations such as 2-pin, 3-pin, and 4-pin, making them suitable for a variety of applications, particularly in industries requiring precise control and communication between devices. They are often used in sensors, actuators, and control systems, making them essential in automation, robotics, and machinery systems.
M8 Circular Connectors vs. Other Types of Connectors
There are numerous types of connectors available for industrial use, and each serves a specific purpose depending on the application. Some of the most common connector types include M12 connectors, D-sub connectors, RJ45 connectors, and Faston connectors. Let’s compare M8 connectors with these popular options.
1. M8 Connectors vs. M12 Connectors
Both M8 and M12 connectors are circular connectors, but the M12 connector is larger, with a 12mm diameter, and typically features more pins (up to 12) than the M8.
M8 connectors are typically used for smaller, less complex systems that require a compact connection, like sensors, small actuators, and devices with low current demands. They are ideal for applications with limited space and provide a high level of protection against environmental factors such as moisture, dust, and vibration.
On the other hand, M12 connectors are used for heavier-duty industrial applications. These connectors can handle higher currents and provide a more robust connection, often used in larger control systems, networking equipment, and more complex automation setups.
Key Differences:
- Size: M8 connectors are smaller (8mm in diameter) compared to M12 connectors (12mm in diameter).
- Current Capacity: M12 connectors are better suited for higher-power applications, while M8 connectors are often used for lower-power, compact systems.
- Pin Count: M12 connectors generally offer more pins than M8 connectors, allowing for more complex connections.
2. M8 Connectors vs. D-Sub Connectors
D-sub connectors are rectangular connectors commonly used in both industrial and IT applications. They have a wider range of sizes, typically between 9 to 37 pins, and are often used in data transmission or communication systems. D-sub connectors are often found in legacy systems, but they are also used in some modern industrial applications.
While D-sub connectors are highly versatile for a range of electrical systems, M8 connectors are more compact and better suited for sensor connections and small machinery. They are also more environmentally resistant, offering better protection against moisture, dust, and vibration compared to D-sub connectors.
Key Differences:
- Shape: M8 connectors are circular, while D-sub connectors are rectangular.
- Application: M8 connectors are ideal for industrial sensor systems and smaller control systems, while D-sub connectors are more often used for data and signal transmission in computers and legacy industrial systems.
- Environmental Protection: M8 connectors provide higher protection against environmental elements.
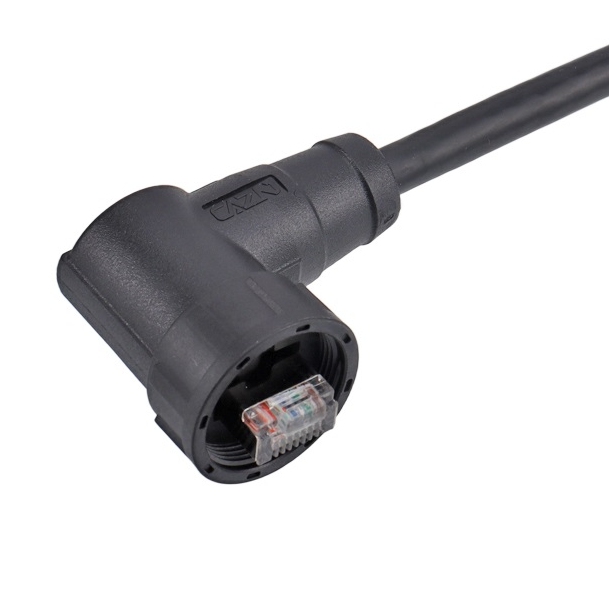
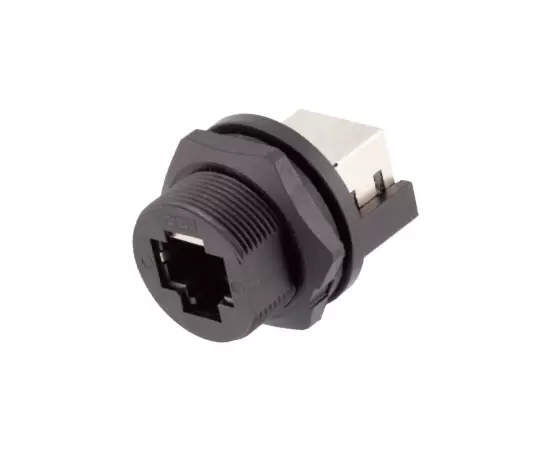
3. M8 Connectors vs. RJ45 Connectors
RJ45 connectors are most commonly associated with networking and data transmission, particularly in Ethernet-based systems. RJ45 connectors are designed for high-speed data transfer, making them an essential component in telecommunications and IT infrastructure.
While M8 connectors are designed for industrial control systems, sensors, and automation, RJ45 connectors are not typically used for direct power or sensor-based connections. In contrast, M8 connectors excel in industrial environments where power, signal, and environmental protection are critical.
Key Differences:
- Function: M8 connectors are used for power and signal connections in industrial systems, while RJ45 connectors are primarily used for networking and data transfer.
- Use Case: M8 connectors are commonly found in automation, sensors, and smart manufacturing, while RJ45 connectors are used in networking, telecommunications, and office IT systems.
- Protection: M8 connectors have a high degree of protection against dust, moisture, and vibration, whereas RJ45 connectors are not as rugged.
4. M8 Connectors vs. Faston Connectors
Faston connectors are typically used in applications where quick and easy connections are needed. They are flat, tab-style connectors commonly found in automotive, appliance, and consumer electronics.
Unlike M8 connectors, which are designed for industrial control and sensor applications, Faston connectors are not as versatile for demanding industrial environments. M8 connectors offer better protection against environmental factors such as dust and moisture, making them the more suitable option for high-performance, high-precision industrial systems.
Key Differences:
- Shape: M8 connectors are circular, while Faston connectors are flat and tabbed.
- Application: Faston connectors are more common in consumer electronics and automotive applications, whereas M8 connectors are ideal for industrial control systems.
- Durability: M8 connectors offer greater protection from harsh environments compared to Faston connectors.
Why Choose M8 Circular Connectors?
M8 connectors are an ideal choice for industries where compactness, reliability, and environmental protection are essential. Their primary advantages include:
- Compact Design: M8 connectors save space, making them perfect for applications where space is limited.
- Rugged Performance: With IP67 ratings and robust sealing, M8 connectors are designed to withstand harsh conditions such as moisture, dust, and vibrations.
- Wide Range of Applications: From wind power generation and high-speed rail to automotive manufacturing and smart manufacturing, M8 connectors are widely used in industries that require dependable, efficient, and long-lasting connections.
- Ease of Installation: M8 connectors are easy to install, offering both standard and custom solutions tailored to your specific needs.
CAZN Electronic: Your Trusted Connector Supplier
As a professional enterprise focused on industrial connection technology, CAZN Electronic specializes in providing high-quality connectors for industries like wind power, high-speed rail, automotive manufacturing, smart transportation, and smart manufacturing. With a deep commitment to following international standards such as IEC, GB/T, and UL, CAZN Electronic ensures that their connectors meet the highest industry requirements.
Whether you need M8 circular connectors, M12 connectors, or other types of industrial connectors, CAZN Electronic provides comprehensive solutions that cater to your specific needs. As a leader in the industrial connector market, CAZN is dedicated to offering cutting-edge technology that powers industries forward.
Conclusion
When choosing connectors for your next industrial project, understanding the key differences between connector types is crucial. M8 circular connectors stand out due to their compact size, rugged performance, and suitability for demanding environments. Whether you’re in the wind power, automotive, or smart manufacturing sectors, M8 connectors provide reliable and efficient solutions for your most challenging applications.
By partnering with CAZN Electronic, you can ensure that your connectors meet the highest standards and are tailored to your unique project requirements. Choose M8 circular connectors for compact, durable, and high-performance connections that will power your projects forward with reliability and precision.